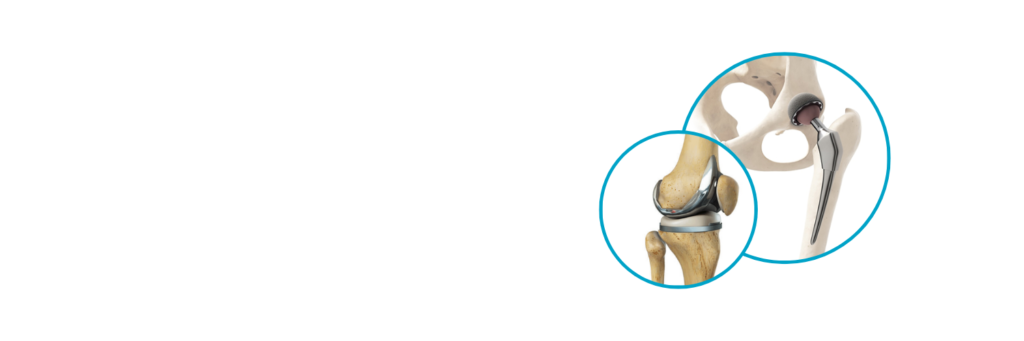
A hip replacement is designed to address symptoms such as hip pain and stiffness, which are often associated with conditions such as arthritis and other forms of joint damage.
Hip arthritis affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic condition that can lead to severe pain, inflammation, stiffness, and immobility. Your doctor may recommend a hip replacement if your symptoms are significantly impacting your ability to carry out your normal daily activities and your quality of life. A hip replacement may also be recommended due to other hip conditions, such as injury, osteonecrosis, or a tumor.
The severity of the joint condition will determine whether a total or partial hip replacement is necessary. It is important to understand the differences between these two types of procedures to allow you to make an informed decision about your treatment.
Partial Hip Replacement
Partial hip replacement surgery, also known as a hemiarthroplasty, replaces only the damaged part of the hip joint. This is usually done when the ball (the head of the femur) of the joint is severely damaged, but the socket (acetabulum) is still healthy. The surgeon may choose to use a ceramic or metal ball and a metal stem to attach it to the thigh bone. This type of surgery is less invasive than total hip replacement and has a shorter recovery time. It may be recommended for patients who have a medical condition that makes total hip replacement too risky or if the hip joint is only partially damaged.
Total Hip Replacement
Total hip replacement surgery involves replacing both the ball and the socket of the hip joint. The surgeon removes the damaged bone and cartilage and replaces them with prosthetic parts best suited to your needs, which may include a ceramic or metal ball, a metal stem, and a metal, ceramic, and/or plastic socket. This procedure is more invasive than a partial hip replacement and requires a longer recovery time. However, total hip replacements are more durable and provide better long-term results. This procedure is often recommended for patients who have severe osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis.
Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement Surgery
In some cases, a patient may be a suitable candidate for a minimally invasive hip replacement procedure. This type of surgery aims to minimize the impact of surgery on healthy tissues, such as muscles and blood vessels, by using much smaller incisions to access the hip joint and by moving the muscles aside. Minimally invasive hip replacements are associated with less pain, a quicker recovery, and a lower risk of complications when compared with traditional surgical methods. In traditional hip replacement surgery, a larger incision is used, and some muscles and tendons may need to be detached to gain access to the hip joint. This can mean a much longer recovery.